What is impacted Teeth? and Symptoms of impacted teeth
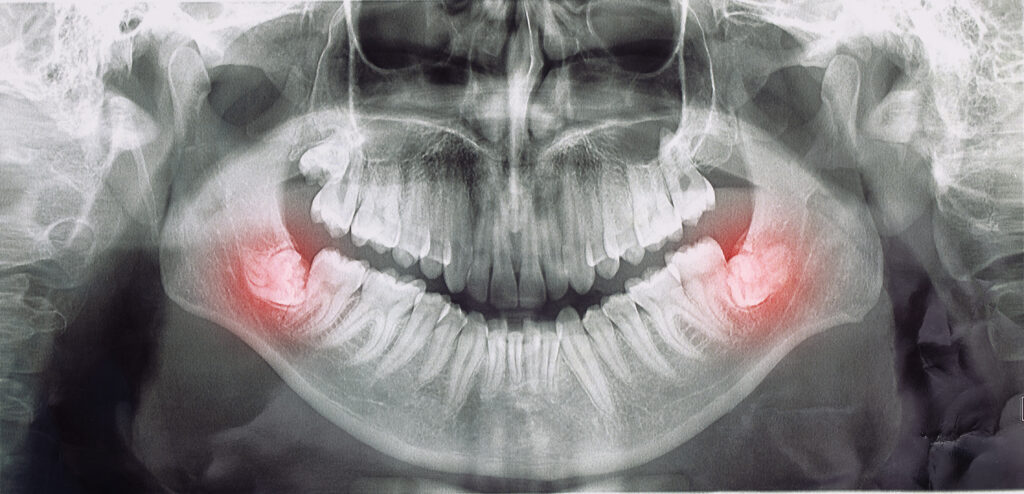
Impacted teeth are teeth that we expect to erupt into our mouth but do not erupt for a variety of reasons and instead remain in our jaws under the gum or bone.
The most common impacted teeth are the wisdom teeth. Canine teeth, premolars, and extra teeth known as’surnumerers’ may also be found in our jaws.
Impacted teeth, particularly those in the bone, are not noticed by the patient, are not visible in the mouth, and are only detected in films taken during routine dentist visits. If you notice a missing tooth in your dental row despite not having had a tooth extracted, it is highly likely that this tooth is also impacted in your jaws.
What is impacted Teeth?
Impacted teeth refers to teeth that do not erupt into the mouth properly. They remain fully or partially embedded in the jawbone or gums. The most commonly impacted teeth are wisdom teeth, or the third molars. But canines and premolars can also become impacted.
There Are Several Reasons Why Teeth May Become impacted
Lack of space: The jaw may be too small to accommodate the third molars, so they get stuck under the gums. This is a common cause of wisdom teeth impaction.
Obstruction: The eruption path of the tooth may be blocked by another tooth. For example, the second molar could block the wisdom tooth from erupting.
Abnormal positioning: The tooth may be angled in the wrong direction, facing horizontally, vertically, or other unusual positions. So it fails to erupt properly.
Over-retention: The tooth remains embedded in the jaw past the usual time of eruption. Sometimes there is no identifiable cause for the over-retention.
Genetics: Impacted teeth seem to run in families and may have a genetic component. Some people are more prone to having teeth that become impacted.
Symptoms of impacted teeth
Impacted teeth, including impacted wisdom teeth, may not always cause noticeable symptoms, but when they do, some common signs and symptoms include:
- Pain or tenderness in the gums or jawbone near the affected tooth
- Swelling or redness in the gums or jaw
- Difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing
- Bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth
- Headache or earache
- Crowding or shifting of adjacent teeth
- Infection or abscess in the gums or jawbone
- Development of a cyst or tumor around the impacted tooth
In which cases should impacted teeth be removed?
- Wisdom teeth, in particular, are frequently impacted due to a lack of space in our jaws. Semi-implanted wisdom teeth, or wisdom teeth with some visible inside the mouth and the rest under the gum, are susceptible to gingival infection. Food accumulation and compression are common under the gingiva from the part of the mouth that enters the mouth, and infections known as ‘pericoronitis’ are common in the gingiva and surrounding tissue in the region. Pericoronitis symptoms include redness around your wisdom tooth, swelling, a bad odor coming from the area, pain radiating to the ear, difficulty swallowing, and swelling in the lymph nodes.
- Presence of teeth that are at an angle to compress neighbouring teeth / have the potential to erupt / cause pressure-like pain
- They can cause cavities in neighboring teeth, as well as harm the roots of these teeth by pushing on them, produce pain or compress our other teeth, and induce crowding in the teeth.
- Follicles are the structures that give rise to our teeth during the development process. The expansion of these structures known as follicles sets the ground for the creation of cysts in the jaws, therefore impacted teeth must be removed in this case.
- Impacted teeth may need to be excised to provide room in the jaws for orthodontic treatment or to avoid pressure/force on properly aligned teeth following orthodontic treatment.
- ıf the impacted tooth belongs to a teenager. Removing impacted teeth in younger patients often leads to quicker healing, shorter surgery time, and fewer complications.
- If the impacted tooth is in an unusual position. Teeth that are horizontally impacted or at an angle often require removal. They can be difficult to clean and may damage nearby teeth.
- If orthodontic treatment is planned. Impacted teeth may need to be removed to allow enough room for orthodontic treatment to properly align the remaining teeth
- If the impacted tooth is causing pain or discomfort. Impacted teeth that become painful or sore often need to be extracted.
- If the impacted tooth is causing infection. Periodontal disease and infections can develop around impacted teeth, so removal is recommended in these cases.
Is impacted tooth surgery difficult?
The ease-difficulty degree of impacted tooth surgery varies according on the impacted tooth’s position, depth, and angle. While teeth embedded in the gum or on the surface require a very short surgical procedure, deeply embedded and angled teeth require a longer surgical procedure, but even in the most difficult positioned impacted tooth surgery, pain-pain is not felt during the procedure with the correct anaesthesia technique. The severity of impacted tooth surgery influences the swelling and subsequent discomfort that the patient experiences. This soreness and swelling are common and anticipated problems that may be managed with your doctor’s advice.
What should be considered after extraction of impacted tooth?
- The tampon placed in the extraction site should be removed after 30-45 minutes and nothing else should be placed in its place.
- Food should not be eaten until the numbness in the extraction area disappears. For 1 day, food should not be eaten with the side of the operation area.
- During the day of the extraction, very hot or very cold food and drinks should not be consumed, warm and soft foods should not be consumed.
Are impacted Wisdom Teeth Harder to Remove?
The degree of difficulty in removing impacted wisdom teeth can vary depending on a number of factors, including the position and angle of the teeth, the shape and density of the surrounding bone, and the patient’s age and overall oral health. In some cases, impacted wisdom teeth may be very close to important nerves or other structures, which can increase the risk of complications during the extraction procedure.
Are non impacted Wisdom Teeth Easier to Remove
Yes, in general, non-impacted wisdom teeth are easier to remove than impacted ones. Non-impacted wisdom teeth are fully erupted and have emerged through the gums, which makes them more accessible and visible for the dentist or oral surgeon to remove.
Compared to impacted wisdom teeth, non-impacted wisdom teeth usually require less surgical intervention and may be removed using a simple extraction technique. During a simple extraction, the tooth is loosened using a dental instrument called an elevator and then removed using forceps. The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia and is relatively quick and straightforward.
You may be interested in: Dental implants Turkey